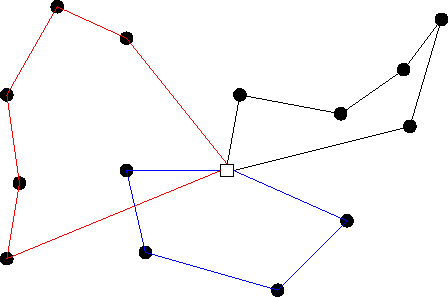
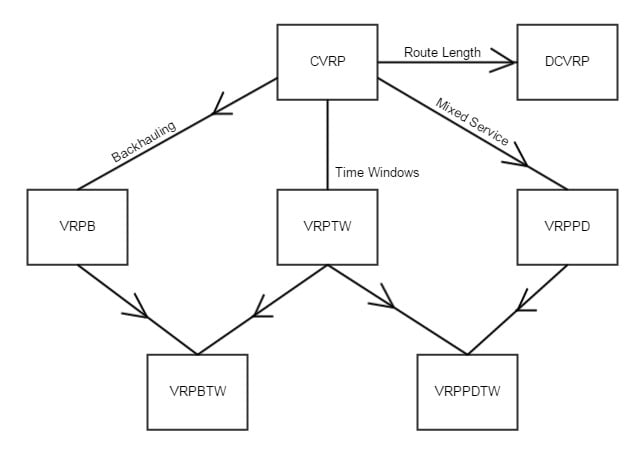
The Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) has been a significant challenge for field service businesses for decades.
It may sound like a straightforward business issue, but it is deeply complicated due to multiple parameters and resource constraints.
For instance, let’s say you have nearly 1,000 deliveries to make every day using 20 vehicles.
How do you determine which vehicles serve which deliveries and in what order?
All this must be done while factoring in fuel consumption, peak traffic times, road conditions, and specific time windows for each customer.
In real life, route planning is fraught with uncertainties, such as fluctuating customer demands, traffic jams, and unexpected weather conditions.
Worse yet, the complexity grows exponentially as the number of vehicles and customers increases.
Solving the VRP is crucial for the seamless movement of goods and services, but finding the right solution is a Herculean task. So, how can you solve the dynamic VRP effectively?
Before we dive into advanced solutions, let’s start with the basics: what is the VRP?
Table of Contents
What Is the Vehicle Routing Problem?
The VRP involves determining the optimal routes from a depot to multiple destinations, each with specific operational or business constraints. These constraints include cost controls, vehicle limitations, route length, and time windows.
[By PierreSelim. – Own work., Public Domain]
While the term “VRP” was coined in the 1950s, its roots trace back to the traveling salesman problem in the 1800s.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the most common VRPs and the tools you can use to unravel them.
What Are the Common VRPs?
Below are some real-life Vehicle Routing Problems that field service businesses face daily:
Vehicle Routing Problem with Time Windows (VRPTWs)
1. Vehicle Routing Problem with Time Windows (VRPTWs) Customers often require their deliveries within a specific timeframe. This means your drivers must show up at the customer’s location within the designated time window.
- Soft time windows: Deliveries outside this window incur penalties.
- Hard time windows: No deliveries can be made outside the designated time.
- Disjoint time windows: Multiple windows exist, requiring drivers to potentially wait for the next available slot.
- Multiple time windows: Non-overlapping periods of various lengths.
Real-Life Scenario:
Consider FedEx. A parcel arrives in the destination country and needs final-mile delivery within a specific time frame—say, Wednesday from 10 to 11 a.m. The courier driver must meet this window while delivering 15 other packages with their own specified timeframes.
Approach to Solution
The key is to find the shortest and most cost-efficient routes while adhering to all time constraints, ensuring maximal customer satisfaction.
2. Pickup and Delivery Vehicle Routing Problem (PDVRP)
On-demand delivery businesses must frequently plan routes, often multiple times a day. This requires balancing multiple factors, including delivery and pickup points, to minimize travel time and fuel costs.
Real-Life Scenario:
Consider Uber. The system must efficiently assign drivers to pick up passengers, optimizing for minimal wait times and travel distances.
Solution Approach:
Assign optimal routes to drivers for picking up and dropping off customers, meeting service requests promptly by minimizing route lengths.
3. Capacity Constraint Vehicle Routing Problem (CVRP) Each vehicle has a maximum load capacity for weight and volume. The challenge is to maximize the number of deliveries without exceeding these limits.
Real-Life Scenario: Take Tesco, a major grocery retailer. Their delivery vehicles must transport goods on pallets. Each vehicle has limited capacity, yet demand from different business units varies significantly.
Solution Approach: Assign routes to vehicles that keep within their capacity limits while ensuring the shortest routes possible to meet all delivery needs.
[By Lady-Shirakawa. CC BY-SA 3.0, Link]
Why Is the VRP Difficult to Solve?
In reality, these VRP types often overlap, significantly complicating solutions.
For example, the order and placement of delivery and pickup addresses can affect vehicle capacity and time windows, creating a combinatorial optimization problem fraught with uncertainties.
Why Do You Need An Effective Solution for VRP?
Effective VRP solutions offer several advantages:
- Reduced logistics expenses
- Sustainable growth
- Enhanced efficiency and productivity
- Time savings and improved customer satisfaction
- Increased revenue and profitability
How to Solve the Vehicle Routing Problem
There are a couple of solutions to address the VRP, such as:
Manual Solving (including Google Maps)
Manual Solving: While experienced drivers might piece together routes manually, this is inefficient and error-prone. A basic tool like Google Maps helps with navigation but cannot handle complex routing for large fleets.
Learn if Google Maps is right for your delivery business.
Preset Solvers
Preset solvers offer a better method than manual planning but often only address a few basic constraints. They are more suitable for academic purposes rather than practical, real-world applications.
Route Optimization Software
Route optimization software, or vehicle routing software, is the most effective solution. Such software can solve complex VRPs quickly, offering routes that save time, cut costs, and meet all time and capacity constraints.
Want To See For Yourself How Route4Me Can Boost Your Profits?
How to Choose the Right Map Route Planner to Solve the VRP
Consider the following core functionalities when evaluating route planners:
Visualization of Route Plans: A visual route planning process lets you see customer locations, drivers, and the impact of route changes instantly. Choose software that allows easy modifications.
Advanced Algorithm: An AI-powered algorithm will create optimal routes, considering all constraints and saving on fuel and drive time.
Proof Of Delivery
Features like eSignatures help drivers capture customer signatures electronically, providing digital proof of delivery.
ALSO READ: Proof of Delivery – Advantages and Benefits
Real-Time Tracking
Real-time tracking allows you to monitor vehicles and drivers, enabling you to re-adjust routes or update ETAs as needed.
ALSO READ: 4 Ways Vehicle Location Tracking Can Reduce Your Expenses and Improve Productivity
Geocoding Capabilities
Ensure your route planner has geocoding capabilities to auto-correct wrong addresses and ensure accuracy.
For more comprehensive insights, consider our detailed article: How to Choose the Best Route Planner.
ALSO READ: How To Eliminate Costly Mistakes Caused By Incorrect Addresses And Drop-off Locations
In order to ensure that you pick a delivery scheduling software that really works for you, consider eighteen more points as laid out in our article: How to Choose the Best Route Planner.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Vehicle Routing Problem
What is the Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP)?
Why is solving VRP important for businesses?
What are some common types of VRP?
How do route optimization software solutions address VRP?
What industries benefit from solving VRP?
Conclusion about the Vehicle Routing Problem
Even the most experienced managers and drivers can’t always anticipate road conditions and customer requests. An advanced tech solution that plans and tracks routes efficiently is crucial. A route optimizer makes solving VRPs easier, enhancing productivity and customer satisfaction.